| Glossary
of Power Terms |
 Information for this page provided by Exide Electronics, Raleigh, North Carolina. Information for this page provided by Exide Electronics, Raleigh, North Carolina. |
| Blackout |
A zero voltage condition lasting for more than two cycles. Same as a power failure. |
| Brownout |
A steady state RMS voltage under nominal by a relatively constant percentage. |
| Critical Load |
Devices and equipment whose failure to operate satisfactorily jeopardizes the health or safety or personnel and/or results in loss of function, financial loss, or damage to property deemed critical by the user. |
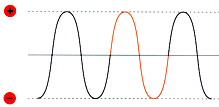
| Cycle |
A
complete AC waveform. See figure below.
 |
| Electrical
Line Noise |
Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) and Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) are unwanted electrical signals that produce undesirable effects in sensitive electronic equipment. |
| Frequency |
The repetition of cycles measure in Hz. 60 Hz is the standard frequency in the U.S. 50 Hz is the standard frequency in other parts of the
world. 60 Hz = 60 cycles per second. |
| Frequency
Variation |
A
change in frequency of more than 3 Hz. |
| High
Voltage Spike |
Rapid
voltage peak up to 6,000 volts with a duration of 100mS to 1/2 cycle. |
| Hybrid
UPS |
Combination of on-line UPS and off-line UPS features. A hybrid UPS has improved performance compared to an off-line UPS, but lacks the higher performance factors of an on-line UPS. It is commonly called line-interactive or ferroresonant, depending on the technology used. |
| Microsecond |
1,000,000th
of a second (mS). |
| Power Sag |
Voltage below 80% to 85% of rated RMS voltage for one or more cycles. |
| Power Surge |
Voltage above 110% of rated RMS voltage for one or more cycles. |
| RMS Voltage |
The range of usable voltage + or - 170 VAC. |
| Switching Transients |
Rapid voltage peak up to 20,000 volts with a duration of 10mS to 100mS. |
| PROBLEM |
DEFINITION |
VISUAL |
CAUSE |
EFFECT |
SOLUTION |
| |
|
|
|
|
 |
no
protection |
 |
limited
protection |
 |
unlimited
protection |
|
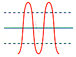
| power surges |
Voltage
above 110% of rated RMS voltage for one or more cycles |
 |
Heavy
electrical equipment being turned off. |
Memory
loss, data errors, flickering lights, equipment shutoff. |
 |
Surge
Protector |
 |
Line
Conditioner |
 |
Standy
battery UPS |
 |
Line
interactive UPS |
 |
On-line
UPS |
|
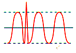
| high
voltage spikes |
Rapid
voltage peak up to 6,000 volts with a duration of 100mS to 1/2 cycle |
 |
Lighning
strikes, switching operations, arcing faults, static discharge. |
Loss
of data, burned circuit boards. |
 |
Surge
Protector |
 |
Line
Conditioner |
 |
Standy
battery UPS |
 |
Line
interactive UPS |
 |
On-line
UPS |
|
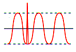
| switching
transients |
Rapid
voltage peak up to 20,000 volts with a duration of 10mS to 100mS. |
 |
Lightning strikes, switching operations, arcing faults, static discharge. |
Memory
loss, data error, data loss, component stress. |
 |
Surge
Protector |
 |
Line
Conditioner |
 |
Standby
battery UPS |
 |
Line
interactive UPS |
 |
On-line
UPS |
|
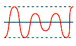
| power sags |
Voltage below 80% to 85% of rated RMS voltage for one or more cycles. |
 |
Heavy equipment being turned on, starting large electrical motors, switching power mains (internal or utility). |
Memory loss, data errors, flickering lights, equipment shutoff. |
 |
Surge Protector |
 |
Line Conditioner |
 |
Standby battery UPS |
 |
Line interactive UPS |
 |
On-line UPS |
|
| electrical
line noise |
Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) and Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) and other frequency causes. |
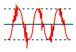 |
Data error, data loss, keyboard lockup, storage loss; system lockup. |
Data error, data loss, keyboard lockup, storage loss, system lockup. |
 |
Surge Protector |
 |
Line Conditioner |
 |
Standby battery UPS |
 |
Line interactive UPS |
 |
On-line UPS |
|
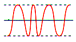
| frequency variation |
A change in frequency of more than 3 Hz. |
 |
Erratic operation of emergency power generators, unstable frequency power sources. |
Disk crash, keyboard lockup, program failures, data corruption. |
 |
Surge Protector |
 |
Line Conditioner |
 |
Standby battery UPS |
 |
Line interactive UPS |
 |
On-line UPS |
|
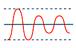
| brownout |
A steady state of RMS voltage under nominal by a relatively constant percentage. |
 |
Heavy equipment being turned on, starting large electrical motors, switching power mains (internal or utility), overloaded circuits. |
Premature hardware failure, data loss and corruption. |
 |
Surge Protector |
 |
Line Conditioner |
 |
Standby battery UPS |
 |
Line interactive UPS |
 |
On-line UPS |
|
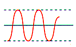
| power
failure |
A zero-voltage condition lasting for more than two cycles. |
 |
Circuit breaker tripped, power distribution failure, utility power failure. |
File corruption, hardware damage, data loss and corruption. |
 |
Surge Protector |
 |
Line Conditioner |
 |
Standby battery UPS |
 |
Line interactive UPS |
 |
On-line UPS |
|




